Lessons from the Field: Navigating Your Move to Microsoft Intune
IT departments are under increasing pressure to manage a growing number of devices, platforms, and user expectations, all while maintaining security and compliance. Traditional on-premises tools like Microsoft Configuration Manager (ConfigMgr) have served organizations well for decades, but the shift to cloud-native solutions is accelerating. Microsoft Intune is at the forefront of this transformation, offering a modern, flexible, and secure approach to endpoint management.
What Is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution that enables organizations to manage user access, devices, and apps from anywhere. It integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 and Azure Active Directory, providing a unified platform for managing Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices.
With Intune, IT teams can enforce security policies, deploy applications, manage updates, and ensure compliance without relying on traditional on-prem infrastructure.
Key Benefits of Migrating to Intune
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Based Management | Manage devices remotely without relying on VPNs or corporate networks. |
| Security and Compliance | Enforce policies, protect data, and meet regulatory requirements. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | Easily support hybrid work environments and scale with organizational growth. |
| Automation and Efficiency | Streamline provisioning, updates, and compliance reporting. |
| Cost Optimization | Reduce infrastructure costs and simplify licensing through Microsoft 365. |
Real-World Use Cases
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Work Enablement | Provision and secure devices for remote employees without shipping them to IT. |
| BYOD Support | Allow employees to use personal devices while maintaining corporate data security. |
| Education and Frontline Workers | Manage shared devices in classrooms or on the front lines with ease. |
| Mergers and Acquisitions | Quickly onboard new users and devices without complex network integrations. |
Transitioning from Configuration Manager to Intune
Many organizations are now choosing to move away from Configuration Manager entirely in favor of a fully cloud-native approach. Here’s why:
On-prem infrastructure is costly and complex to maintain.
Remote device management is limited without VPN or co-management.
Intune offers a more agile, scalable, and future-ready solution.
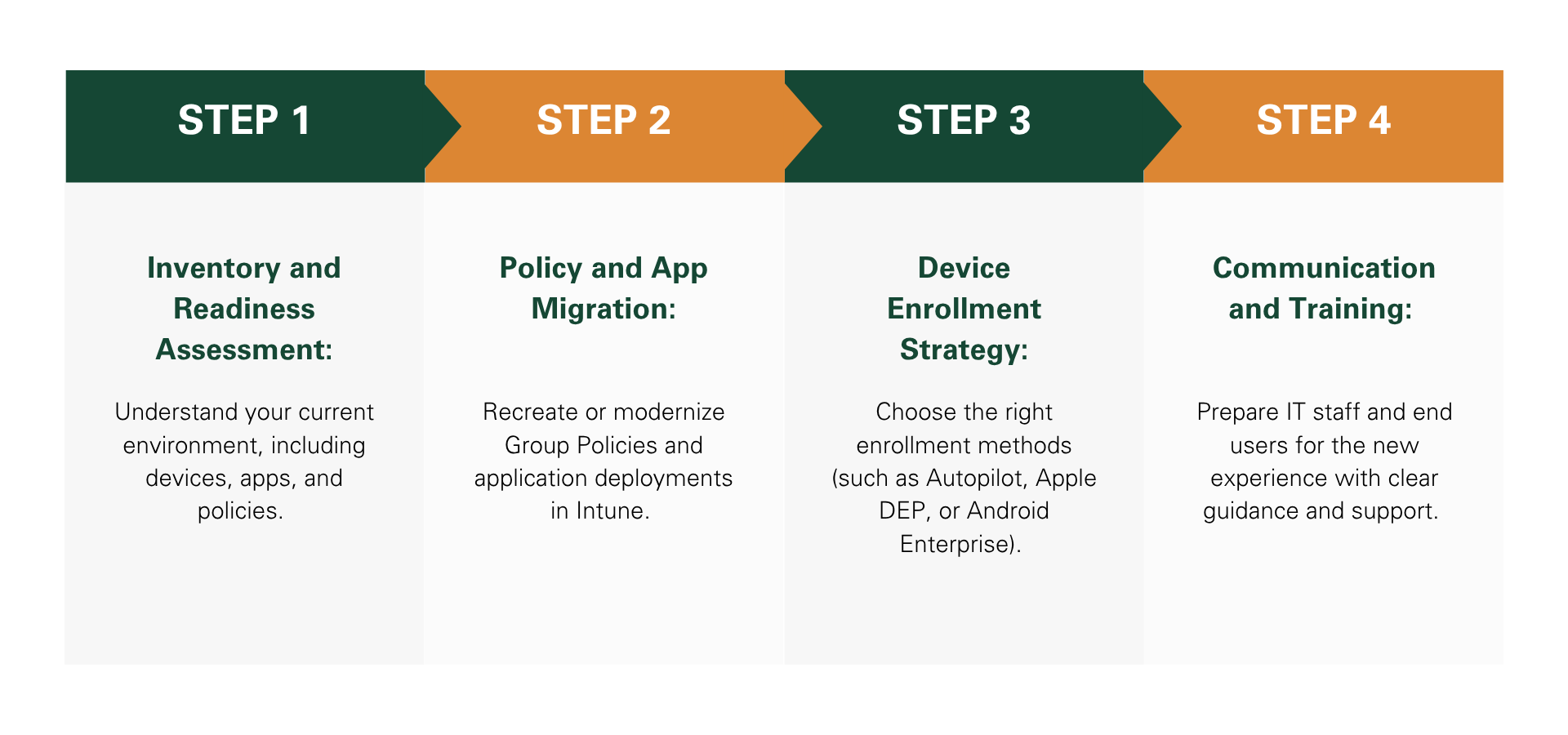
Steps to a Successful Transition
Lessons Learned from Organizations That Have Made the Switch
| Lesson | Insight |
|---|---|
| Start with a Pilot | Begin with a small group of users or devices to validate policies, app deployments, and enrollment methods before scaling. This helps identify issues early and build internal confidence. |
| Communicate Early and Often | Clear communication with stakeholders and end users is critical. Explain the reasons for the change, what to expect, and how it will benefit them. This reduces resistance and confusion. |
| Invest in Training | Ensure IT staff are trained on Intune’s capabilities and management workflows. Empowering your team with knowledge leads to better support and faster adoption. |
| Modernize Policies | Avoid simply replicating legacy Group Policies. Use the migration as an opportunity to streamline and modernize your approach to device configuration and security. |
| Leverage Autopilot and Enrollment Automation | Automating device provisioning with Windows Autopilot or Apple DEP saves time and reduces manual errors. It also improves the user experience during onboarding. |
| Monitor and Iterate | Use Intune’s reporting and analytics tools to monitor compliance, app performance, and user activity. Adjust policies and configurations based on real-world feedback. |
| Expect Some Hybrid Scenarios | Not all systems or workflows will be ready for full cloud management immediately. Be prepared to maintain some hybrid configurations during the transition period. |
| Document Everything | Maintain clear documentation of your migration plan, policies, and procedures. This helps with troubleshooting, onboarding new team members, and future audits. |
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Legacy Dependencies: Some apps or workflows may still rely on on-prem systems. Consider hybrid approaches during the transition and plan for long-term modernization.
User Adoption: Change can be disruptive. Provide training, documentation, and support to ease the transition for end users.
Network and Bandwidth: Cloud management requires reliable internet access. Use delivery optimization and caching strategies to reduce bandwidth impact.
Phased Rollout : Start with a pilot group, gather feedback, and scale gradually. This reduces risk and builds confidence across the organization.
Conclusion
Moving to Microsoft Intune is not just a technical upgrade. It is a strategic shift toward a more agile, secure, and modern IT environment. As the workplace continues to evolve, organizations that embrace cloud-native endpoint management will be better positioned to support their users, protect their data, and adapt to change.